What is L-Carnitine?
Before we discuss what foods provide carnitine, let’s understand it a little bit better. Carnitine, which is generated from an amino acid, is found in nearly all of the body’s cells. Because the component was separated from meat, its name is taken from the Latin carnus, which means “flesh.” L-carnitine, acetyl-L-carnitine, and propionyl-L-carnitine are examples of substances classified as carnitine.
Carnitine is essential for energy synthesis. It carries long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondria to be oxidised (“burned”) for energy production. It also transfers hazardous substances produced by this cellular organelle in order to prevent their buildup. Carnitine is concentrated in tissues that use fatty acids as a dietary fuel, such as skeletal and heart muscle.
L-carnitine is either consumed through animal-based foods or is produced in the liver, kidney, and brain from the necessary amino acids lysine and methionine. L-carnitine demands are approximately 25% met daily. Therefore, supplementation is necessary, either through dietary changes or supplemental nutrients. (1)
Effects of Carnitine on Muscle Recovery
Muscle damage and soreness brought on by exercise can both lower quality of life and restrict further training. L-carnitine has been shown to improve exercise performance in addition to assisting with recovery following exercise through a variety of ways. According to research, following initial intense exercise, power production increased significantly.
Recommended Carnitine Dosage
Because the liver and kidneys create enough carnitine from the amino acids lysine and methionine to meet daily demands, healthy children and adults do not need to take it from food or supplements. Based on Food and Nutrition Board, carnitine is not an essential nutrient.
As nutritional supplements, L-carnitine, acetyl-L-carnitine, and propionyl-L-carnitine are sold over-the-counter. Carnitine is frequently marketed as a supplement to help with weight loss, to increase exercise performance, and to boost overall wellbeing.

What Foods Provide Carnitine?
The finest sources are animal products like red meat, fish, poultry, and milk. Generally speaking, beef has a higher carnitine content. Carnitine is largely present in the whey component of dairy products. (2)
Table below showing carnitine-rich foods.
| Food | Milligrams (mg) |
|---|---|
| Beef steak, cooked, 4 ounces | 56–162 |
| Ground beef, cooked, 4 ounces | 87–99 |
| Milk, whole, 1 cup | 8 |
| Codfish, cooked, 4 ounces | 4-7 |
| Chicken breast, cooked, 4 ounces | 3-5 |
| Ice cream, ½ cup | 3 |
| Cheese, cheddar, 2 ounces | 2 |
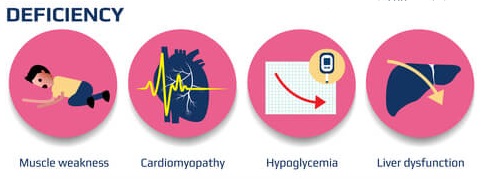
carnitine deficiency
There are two different deficiency conditions. A genetic condition known as primary deficiency which affects the cellular carnitine-transporter system and typically shows symptoms by the time a child is five years old, including cardiomyopathy, skeletal muscular weakness, and hypoglycemia. Secondary deficiency can develop as a result of specific diseases (like chronic renal failure) or environmental factors (like the use of specific antibiotics) that decrease or increase the absorption or excretion of carnitine.
About 60-180 mg of carnitine are consumed daily by adults who consume mixed diets that contain red meat and other animal products. Vegans receive substantially less (about 10–12 mg) due to their avoidance of foods originating from animals. The small intestine absorbs and transports the majority of dietary carnitine (54–86%) into the circulation. (3)
Even diets low in carnitine have minimal effect on the body’s overall carnitine concentration because the kidneys efficiently conserve it. To keep steady blood concentrations, extra carnitine is eliminated in the urine as needed by the kidneys as opposed to being digested.
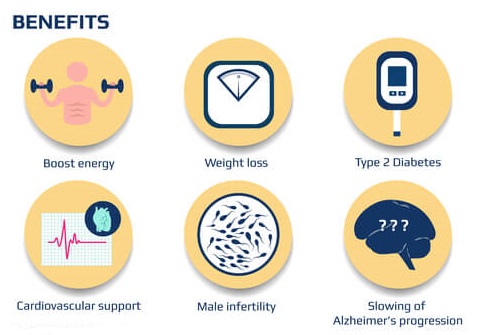
Carnitine Benefits
L-carnitine appears to be quite helpful in treating liver problems since it lowers ammonia levels, alleviates hepatic encephalopathy symptoms, and improves several liver function markers. High dose supplementation has been reported to improve the quality of sperm, and a few studies have found advantages in male fertility. According to one study, L-carnitine appears to improve several symptoms in people with polycystic ovarian syndrome, increasing fertility.
Although additional research is required to understand its true value, acetyl-L-carnitine (and possibly L-carnitine as well, but studies have only employed ALCAR) has some efficacy in reducing the symptoms of depression. In older persons with inadequate muscular endurance, it appears to lessen fatigue; nevertheless, its benefits on athletes during physical activity aren’t very consistent, despite data that suggests slight improvements. L-carnitine may somewhat reduce muscle deterioration during resistance training.
Individual research have not shown particularly impressive results when it comes to fat loss. A little amount of fat loss has been observed in some studies, which is often attributed to increased physical activity brought on by higher energy intake. Blood pressure, blood glucose, insulin sensitivity, blood lipids, oxidative stress, and inflammation appear to be mildly benefited by L-carnitine. (4)
carnitine side effects
Supplemental carnitine can result in nausea, vomiting, cramping in the abdomen, diarrhoea, and a “fishy” body odour at doses of about 3g per day. Rarer adverse effects include seizures in people with seizure disorders and muscle weakness in uremic individuals.
According to certain studies, gut bacteria break down carnitine to create a compound called TMAO that may raise the risk of cardiovascular disease. People who eat meat seem to be more affected by this than people who are vegan or vegetarian.