What’s The Difference?
Grass fed vs grain fed beef nutrition differences have become a myth. The main difference is in the intramuscular fat (IMF) between these two types. Cattle breed or genetic variation has reportedly an impact on the amount of beef IMF and the fatty acid composition. fat accumulation and changes to the feeding plan, such as switching to a grain or grass diet.
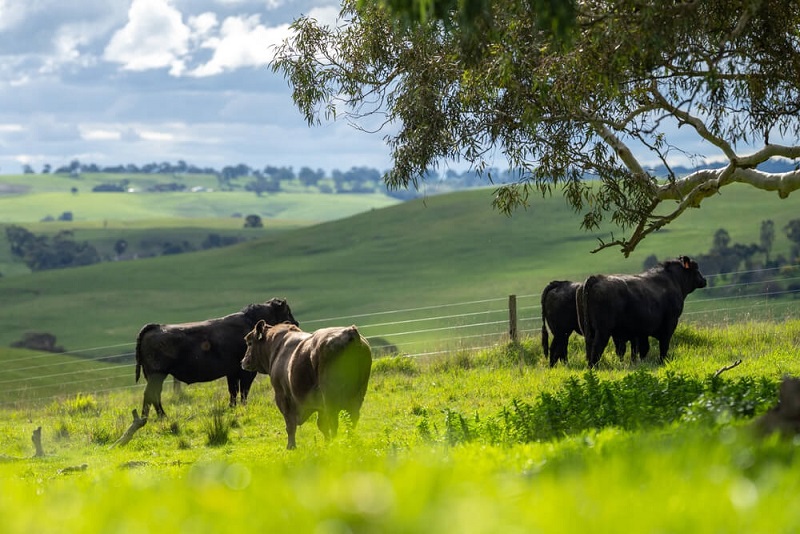
Cattle are raised with concentrate or grain diets from growth through the fattening stage, with grass only provided during the first six months of life to create marbled beef.
Grass Fed vs Grain Fed Beef Nutrition Facts
| Nutrition Facts (100g/3.5 oz) | Grass-Fed Beef Facts | Grain-Fed Beef Facts |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 198 | 290 |
| Protein | 19 | 14 |
| Fat | 11.2 | 16 |
| Carbohydrates | 0 | 0 |
| Sugar | 0 | 0 |
| Fiber | 0 | 0 |
Grain-feeding system
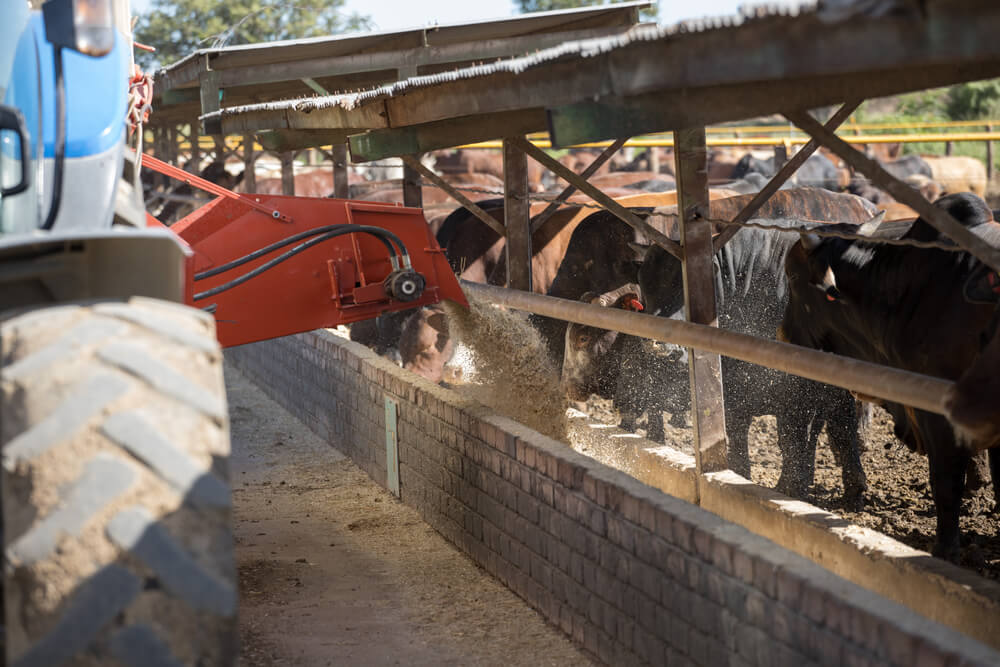

Grass, forage, hay, and some feed additives are commonly provided to calves destined for the beef industry until they are six months old, at which point they undergo a finishing stage with high concentration to attain the necessary weight for slaughter. Between the ages of 6 and 29 months, beef cattle are routinely fed a high-energy diet. Cattle are given a concentrate containing ad libitum rice straw along with a mixture of 71% total digestible nutrient (TDN) and 13% crude protein (CP) during the growing stage (6 to 11 months) and early fattening period (12 to 20 months).
As the final fattening stage approaches, this diet is slightly modified to 73% TDN and 11% CP along with ad libitum rice straw, In the latter phase of fattening (21 to 29 months). To enhance IMF development, cattle are fed a mixture of 10% rice straw and 90% concentrate. (1)(2)
Grass-feeding system
Beef cattle who are fed only grass should rigorously abide by the law that states that animals must have constant access to pasture throughout the growth season and cannot be fed grain or grain byproducts.

why is grass-fed beef better?
- Low in saturated fatty acid (Unhealthy fat): In comparison to grain-fed cattle, grass-fed beef had a 62% lower lipid content, a 65% lower saturated fat, and higher amounts of omega-3 fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA). Saturated fat are composed of a carbon chain without any double bonds. High volume consumption of saturated fatty acid lead to heart disease, increase HDL (bad) cholesterol and cardiovascular disease. (3)(4)
- Rich in vitamins: Grass-fed beef is a good source of several vitamins and elements that support healthy cell growth and cartilage and muscle repair. In addition to being rich in B vitamins, research has shown that grass-fed beef has higher levels of antioxidants such as vitamins A and E than grain-fed cattle.
- High in antioxidants: Grass-fed beef has higher antioxidant levels than grain-fed beef. Antioxidants aid in preventing cell deterioration that can result in life-threatening illnesses like cancer and Alzheimer’s disease.
- Omega-3 fatty acid: It has two to six times as more Omega-3 fatty acid. Many diseases, including heart disease, stroke, autoimmune reactions including lupus, eczema, and rheumatoid arthritis, as well as a variety of other ailments, have been discovered to be prevented or treated by omega-3 fatty acids.
- Helps in muscle growth & recovery: Every amino acid your body requires to create a complete protein building block is present in beef. As a result, it is a good source of protein. Grass-fed beef’s protein can aid in preventing sarcopenia, a condition that results from a long-term protein deficit and results in a loss of muscle mass, as part of a healthy lifestyle that also includes appropriate eating and exercise habits.
Beta-alanine, an amino acid found in beef, aids in the formation of carnosine by your body. Carnosine is crucial for the health of your muscles, potentially enhancing your ability and performance during intense activity. According to studies, using large dosages of beta-alanine supplements for 4 to 10 weeks increases carnosine levels in muscles by 40–80%. In humans, high levels of carnosine have also been associated with reduced fatigue and improved muscle function. - Rich in iron: Grass-fed beef is rich in iron, particularly a form of iron known as heme iron, which the body readily absorbs. Anemia, a disorder in which the blood has fewer red blood cells and a lower ability to carry oxygen, can be brought on by an iron shortage. Weakness and fatigue are the main signs of anaemia.
disadvantages of grass-fed beef
Grass-fed beef may contain greater amounts of fat and cholesterol than other meats, although having less saturated fat than grain-fed cattle. Grass-fed beef should be consumed in moderation, just like all other foods. Colon cancer is one the most common cancers in the world which could happen by high consumption of beef. Humans can become infected with tapeworms by eating raw or undercooked beef, which is called parasite infection.
Conclusion
Beef from cattle fed a diet high in grass contained less total fat than beef from calves fed grains. The beef’s fatty acid composition for human consumption had been significantly impacted by the lowering of total fat content. When compared to the same 100 g of beef from grain-fed cattle, grass-fed beef had 2,773 mg less total SFA. In comparison to grain-fed beef, grass-fed beef had a more favorable SFA lipid profile, with less of the fatty acids that raise cholesterol and less of those that lower cholesterol. Grass-fed beef has higher levels of omega-3, and long-chain n-3 Polyunsaturated fat acid than grain-fed cattle in terms of these crucial fatty acids for human health. (5)