sleep and muscle recovery study
This article shows how does sleep affect muscle growth and recovery. The followings are the 4 science based facts.
1. Metabolism Reduction
Lack of sleep increases the risk of metabolic dysfunction and the loss of muscle mass and function. Complete sleep deprivation quickly impairs your brain ability to focus, whereas sleep restriction affects body’s stability and has both short and long term negative effects on metabolism. The majority of metabolic tissues, such as the liver, adipose tissue, and skeletal muscle, are susceptible to the negative effects of sleep deprivation. (1)
Human metabolism is mostly regulated by skeletal muscle. Sleep deprivation and restriction have the potential to have a significant impact on muscle health through affecting gene regulation and substrate metabolism. Even brief sleep deprivation (less than a week) can affect glucose metabolism, lower insulin sensitivity, and impair muscular performance. Skeletal muscle is composed of 80% proteins, hence maintaining optimal muscle protein metabolism is equally important for muscular health. (2)
2. Increase Injury Possibilities
Muscle weakness has been identified as an independent risk factor for falls, hip fractures, and negative physiological alterations such as glucose intolerance and bone mineral density loss. Furthermore, based on the incidence of disability, morbidity, and mortality in adult populations, loss of muscle strength is a strong indicator of health status. Individuals with better muscle strength are less likely to suffer from disability and joint dysfunction. Furthermore, these people live longer than those with poor muscle strength. A previous study found that even in middle-aged people, those with lower strength had more than twice the risk of death as those with higher strength. (3)
- Is 6 hours of sleep for muscle growth enough?
Sleep quality was related with enhanced muscle strength, but short sleep duration was associated with an increased risk of muscle weakness. Given that long periods of sleep were not recommended, a sleep duration of 7-8 hours may be optimal for muscle strength. Reduced sleep quality and duration may be risk factors for muscle strength.
3. lower muscle protein production
In a group of healthy young people, even one night low quality sleep dramatically lowered muscle protein production. Complete sleep deprivation is known to reduce muscle mass, muscle fiber cross-sectional area, and protein synthesis pathway indicators.
4. Reduce Testosterone Production
Research claims that, one night of sleep deprivation can reduce up to 24% of testosterone production in males. Testosterone level is directly linked to muscle strength and mass, therefore low testosterone level leads to loss of muscle mass. (4)

does napping help muscle growth
Evening naps were discovered to be more probable than morning and afternoon naps to increase growth hormone levels in your body. So, if you want to increase HGH production, attempt to take naps in the evening. However, the extent to which napping affects your muscle growth is determined by the quality of your naps.
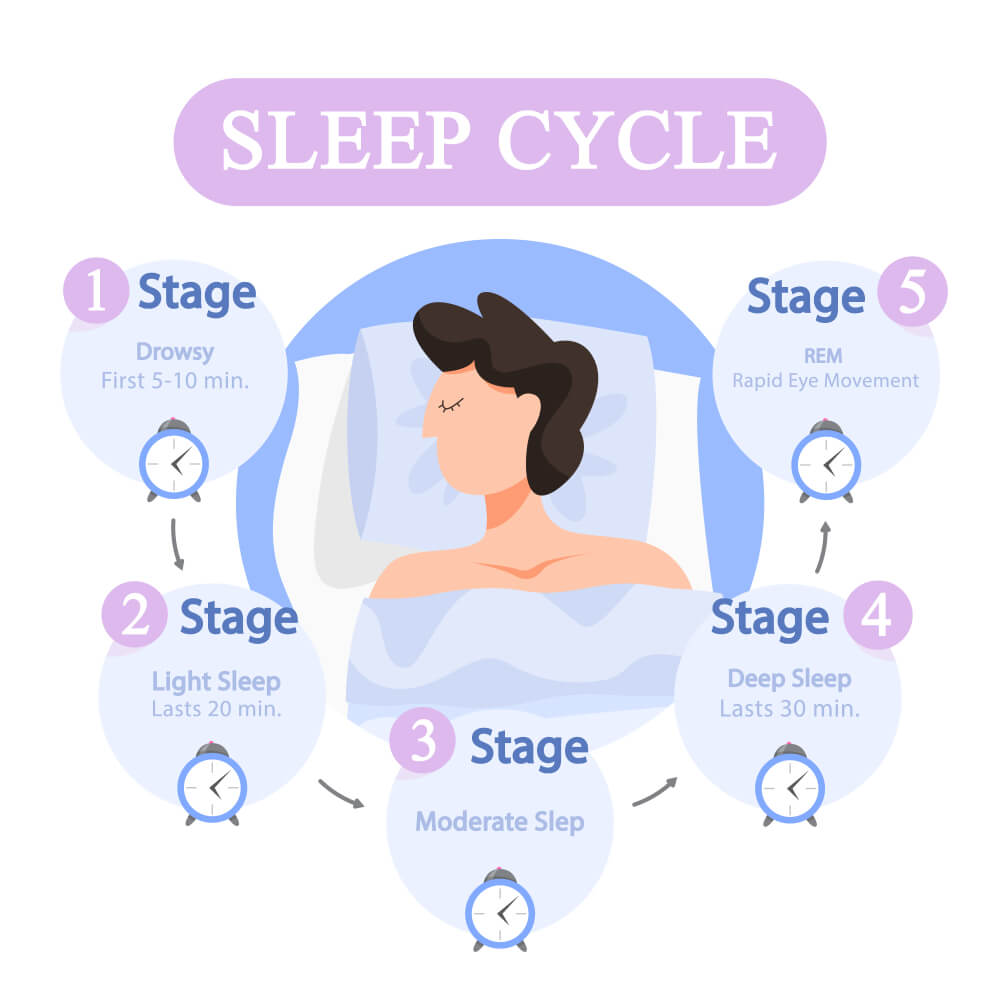
Stages of Sleep
Wake, N1, N2, N3, and REM are the five stages of sleep. Non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep is classified as stages N1–N3, with each level becoming deeper. The NREM stages account for around 75% of sleep, with the majority of time spent in the N2 stage. A typical night’s sleep consists of four to five sleep cycles, with sleep phases progressing in the following order: N1, N2, N3, N2, REM. A whole sleep cycle takes about 90 to 110 minutes. The first REM session is brief, but as the night progresses, larger REM periods and less time in deep sleep (NREM) occur. (5)
Conclusion
Lack of sleep has been associated to a variety of metabolic effects. Total sleep loss causes anabolic resistance in young boys and girls by lowering muscle protein production after meals. Sleep deprivation also induced a catabolic environment, shedding light on the mechanisms behind this process.