What are the 3 types of metabolism?
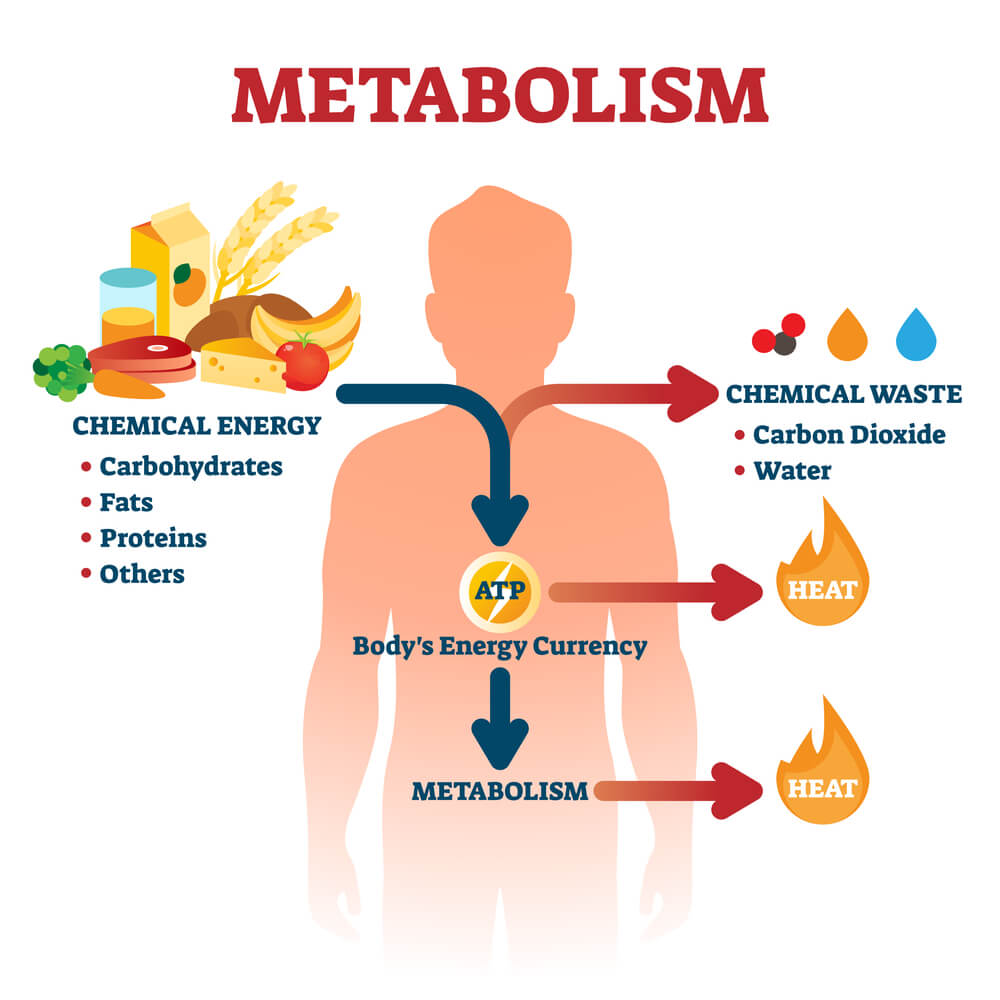
3 types of metabolism in humans include carbohydrate, lipid and amino acid metabolism which will be explained in details later in this article. The term “metabolism” refers to the whole of the chemical reactions that take place inside each cell of the body and supply the organism with energy. This energy is needed to synthesize new organic material and power essential operations.
The metabolic processes support both growth and reproduction as well as the upkeep of living things’ structural integrity. The metabolic processes allow organisms to react to their surroundings. Energy is required for all chemical processes carried out by living things, including digestion and the movement of materials from one cell to another.
By ingesting nutrients and other elements that serve as the building blocks for movement, growth, development, and reproduction, every living thing depends on its surroundings to thrive. Enzymes, which are proteins with specialized roles in anabolism and catabolism, mediate all of these processes. The rate at which energy is produced is known as the basal metabolic rate, and it is influenced by things including sex, race, activity level, diet, age, and illnesses like sepsis or cancer. (1)
In terms of categories, there are two types of metabolism with example
- Catabolism: Larger organic compounds are primarily broken down into smaller molecules during this process. The metabolism in question produces energy.
Example: Catabolic processes include glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, the breakdown of muscle protein to use amino acids as substrates for gluconeogenesis, the breakdown of fat in adipose tissue to fatty acids, and the oxidative deamination of neurotransmitters by monoamine oxidase. - Anabolism: The basic goal of this process is to create complex chemicals from simpler ones that the cells need. This metabolic process needs energy, which is also stored.
Example: Gaining muscular mass and mineralization of the bones are two instances of anabolism. Proteins are broken down into amino acids, glycogen is converted to glucose, and triglycerides are converted to fatty acids during catabolic processes.
The chemical processes that underlie metabolism are essentially the same in all living things, including bacteria, fungi, plants, animals, and even some bacteria. Proteins that function as catalysts in certain environmental conditions, such as pH and temperature, mediate all of these chemical processes. DNA serves as the starting point for the production of many of the catalysts that mediate chemical processes throughout our body.
1. Carbohydrate Metabolism
Carbohydrate metabolism concentrates on glucose. A glucose molecule is promptly converted inside of a cell into glucose-6-phosphate, which is unable to leave the cell. Hexokinase (in the liver and pancreas) is the catalytic enzyme in this process. Nearly all metabolic processes, including glycolysis and glycogenesis, can utilize this molecule. Glycogen granules are how carbohydrates are stored so that they can quickly mobilize glucose when needed. Carbohydrate metabolism is regulated mainly by insulin, as it stimulates glycolysis and glycogenesis.
2. Lipid Metabolism
Fatty acids are used in tissues that produce energy by oxidation. They are transported attached to albumin and some of them are potentially poisonous and amphipathic. Micelles of fatty acids are absorbed in the intestines and taken up by the enterocytes that line the intestinal wall. Once inside, these fat molecules are reduced to smaller molecules, including glycerol and free fatty acids, which are later conjugated to form triglycerides. Outside of the enterocyte, they are coupled to proteins to create chylomicrons.
The liver receives these chylomicrons’ high concentration of triglycerides and cholesterol via the portal vein system. A portion of the cholesterol and triglycerides will be extracted from these complicated molecules by the liver. In order to move endogenous lipids and fat to peripheral organs that express hormone-sensitive lipase and lipoprotein lipase, the liver secretes a novel form of the complex molecule known as VLDL.
- VLDL: The liver produces very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) cholesterol, which is then released into the bloodstream to provide the body’s tissues with a particular kind of fat (triglycerides). Each form of cholesterol is a mixture of lipids and lipoproteins.
3. Amino Acid Metabolism
Each day, we eat roughly 100 g of protein. The body processes 300 g of protein daily, or close to 10 kg total. Amino acids are the structural components that make up proteins. Some of these are non-essential amino acids, indicating that the body can synthesis them but must acquire them from the food (which the body can synthesize). The enterocytes take up proteins in the form of amino acids. Amino acids have a nitrogen group and a structure known as 2-oxoacid, which has two carbon atoms.
Ammonium, a hazardous chemical in particular for the central nervous system (CNS), is produced during the metabolism of amino acids. The liver has the ability to digest ammonium for excretion into the ornithine (urea) cycle. Two different chemical reactions involve the metabolism of amino acids. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) are involved in the first process, which is referred to as transamination.
5 Ways to Increase Metabolism
- We must limit our calorie consumption and shed additional pounds in order to be fit and healthy. We eat to provide our bodies the energy they need to function. Too little food might cause our metabolism to slow down and prevent the body from absorbing vital minerals. According to research, excessive dieting causes weight loss that is made up of muscle mass rather than fat mass. (2)
- A healthy breakfast increases metabolism and gives us more energy throughout the day. Those who skip breakfast in the morning are more likely to have low metabolic energy.
- Caffeine can increase our metabolism rate by 5 to 8% by stimulating the central nervous system.
- Researchers claim that fiber can increase fat burning by 30%. More fiber in the diet helps people stay fit and healthy.
- Increased consumption of organic foods like peaches, bell peppers, celery, apples, lettuce, and grapes can speed up our body’s metabolism.
- Metabolic Effectors In Weight Management
There are inherent and extrinsic elements in metabolic pathways that are important in weight return or maintaining weight loss. While intrinsic factors concentrate on energy balance and functional resistance to weight loss, extrinsic factors cover lifestyle and psychosocial aspects. Complex metabolic networks bind the two processes together. Therefore, in people with large baseline fat mass, weight reduction progresses to consistent maintenance of the decreased weight. High fat concentrations cause fat mass to decrease without putting the adipocytes under stress or reducing the amount of fat-free mass. In addition to genetic variability, effective weight loss management strategies must address both intrinsic and extrinsic factors, such as a restricted caloric intake, exercise, a diet low in fat, and adequate sleep.
After a healthy weight has been attained, daily physical activity ranging from moderate to intensive efficiently maintains body composition and weight. Exercise and resistance training are common tactics used in weight-maintenance program to prevent unhealthful weight gain. Exercise produces a reorganization of body fat and a positive energy balance. As a result, this encourages the growth of muscular mass, which can be maintained through consistent exercise training in addition to appropriate dietary practices, adequate sleep cycles, and relaxation.
Recommended For You